La block chain technology, also called technology blockchain, is an information system that is made up of different blocks, providing great utility when establishing histories and records, and offering a very secure and efficient system, especially in the field of economics and carrying out transactions without them existing. intermediaries.

Article Content
What is block chain technology
The name of this technology, in Spanish chain of blocksIt refers to a type of data structure where different blocks are concentrated to which information is added that will be directly related to a previous block.
In this way, a timeline is established that allows complete monitoring of all the information, thus establishing very well-defined parameters and knowing processes not only accurately, but also with maximum security and all guarantees.
This is the main reason why the tecnología blockchain is especially oriented to the field of online financial management.
This system is based on the storage, transmission and confirmation of data.
Types of blockchain technology
La block chain technology We can classify it into four types based on its characteristics:
- Data access: depending on the way in which the data stored in the blocks of the chain is accessed, it may be public or private.
- Permissions: It will depend on the way in which the permissions that will allow the creation of blocks are established, that is, whether these permissions exist or not.
- Combination of access and permissions- This is a combination of all viable alternatives which are public access without permissions, public access with permissions, private access with permissions. In this case, private access without permissions would not exist due to obvious reasons.
- State changes- It will depend on how you can change the database.
Applications of this technology
This technology has a fairly wide field of application that is focused on:
- Cryptographic component: This is what is known as Bulletin Boards, which is a system through which records can be created, electronic voting carried out, information shared through forums or even for online auctions.
- Smart contracts: They will be carried out between peers, allowing the contract to acquire legitimacy. The most prominent platforms in this regard are Ripple and Ethereum.
- Cryptocurrencies: It is established as a notary in transactions, preventing practices such as the use of the same currency on several occasions. Among the most common we find Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin and Ethereum.
- Notary: guarantees the security of transactions, saving them and allowing them to be monitored.
- Name registration: alternative to DNS for creating a secure and easy-to-check database. Namecoin stands out.
As we can see, blockchain technology is called to guarantee any type of movement, carrying out constant registration and verification that guarantees its legitimacy, and acting as a notary both in carrying out different types of transactions and in registering names. .
This guarantees the fluidity of operation and its security, avoiding risks and without having to resort to intermediaries, which saves time, effort and of course money thanks to block chain technology.
Cloud vs Blockchain
Today, we have the cloud, where the services are:
- Physically decentralized
- Hierarchically centralized Results
- Low cost maintenance
- Highly scalable
- Widely used by colleagues and end users
With Blockchain, Internet services are evolving to be:
- Decentralized
- Physically
- Hierarchically
- Immutably
- Safe:
- At the infrastructure level
- At the software level
The evolution of blockchain algorithms
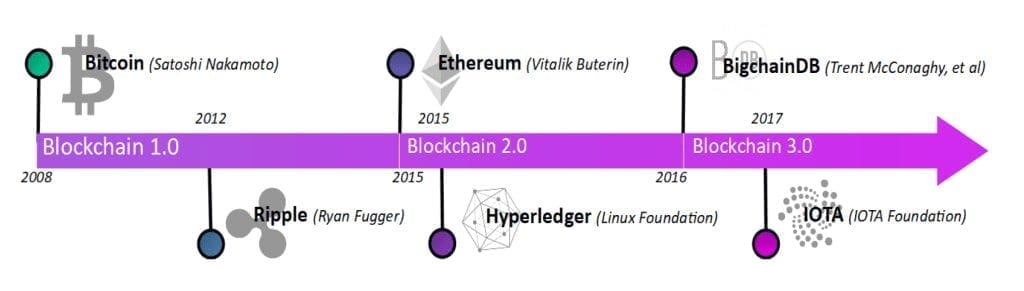
CYGNUS, the first blockchain platform adapted to insurers
CYGNUS has become the first blockchain platform that has been adapted to the insurance sector through the exchange of information between participants (130 insurers and their collaborators: workshops, experts...), which achieves an effective and efficient exchange of information between the same companies in the sector
OPEN FINANCE/PSD2
It allows third parties to access bank information through APIs, creating new businesses and digital ecosystems with the banks' own information. PSD2 has done with banks what the internet has done with collaborative economy platforms.
On September 14, 2019, the second Payment Services Directive (PSD2) came into force. This European regulation has the great merit of leading all European banks to begin opening up to the outside world.
The effects were tangible. In fact, the boards of directors of many European banks began to trust in this great innovation; many banks started working on APIs (finally, since they are a fundamental instrument in the digital age); many financial institutions allocated some legal budgets to manage PSD2 (this part is not very good, because before being a legal or technological problem, PSD2 is a business problem); and a host of startups and some non-banking players (such as some retailers) attempted to exploit its commercial implications.
Comprehensive financing, not just banking
Traditional banking tends to disappear or evolve, the advance of new times will put an end to the past despite its resistance, innovation should not be limited to current account or payment banking services, but should be applied to all financial services , starting with wealth management or financial intermediation, which are the most contiguous, but also the most "innovative" and not purely banking services such as strong authentication, new insurance services or all open commerce.
Many banks are already beginning to realize that they either adapt to change or they will end up dying.
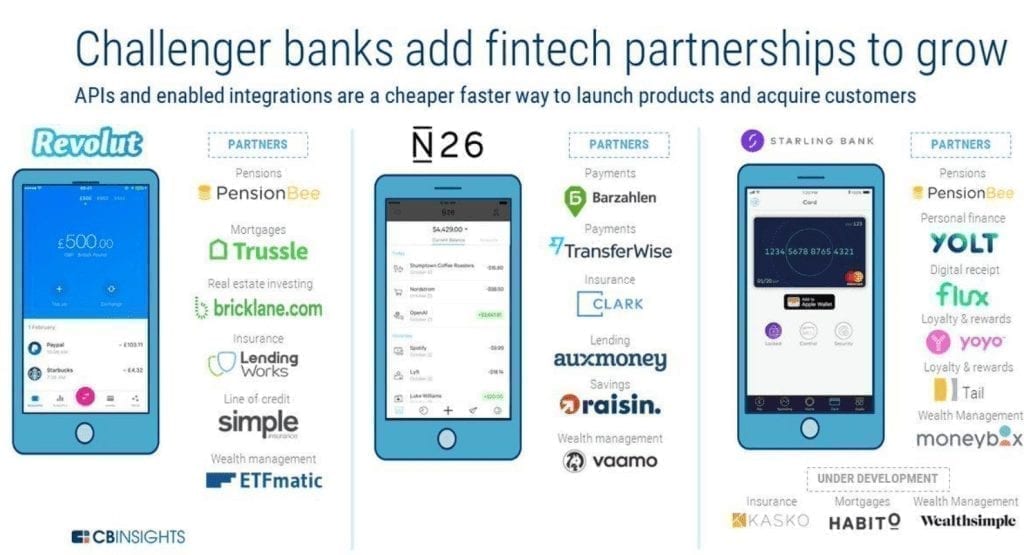
Therefore, the short-term trend is for traditional banks to control bank deposits and credit and debit cards, while Fintech companies control CRM (Users), Marketplaces, investment, mortgages and insurance.

Blockchain + Fintech
Money, as we know it, was a public service whose monopoly was held by the respective issuing banks and national and international regulators. Today everything has changed, what the blockchain really implies in the economy is exchange, coordination, new rules, with contracts that must be unified through perfect synchronization between the stakeholders involved. Smart contracts will lead us to automatic, autonomous and secure agreements, without intermediaries that contribute an expense in the operation with low-cost contracts.
The bitcoin ecosystem
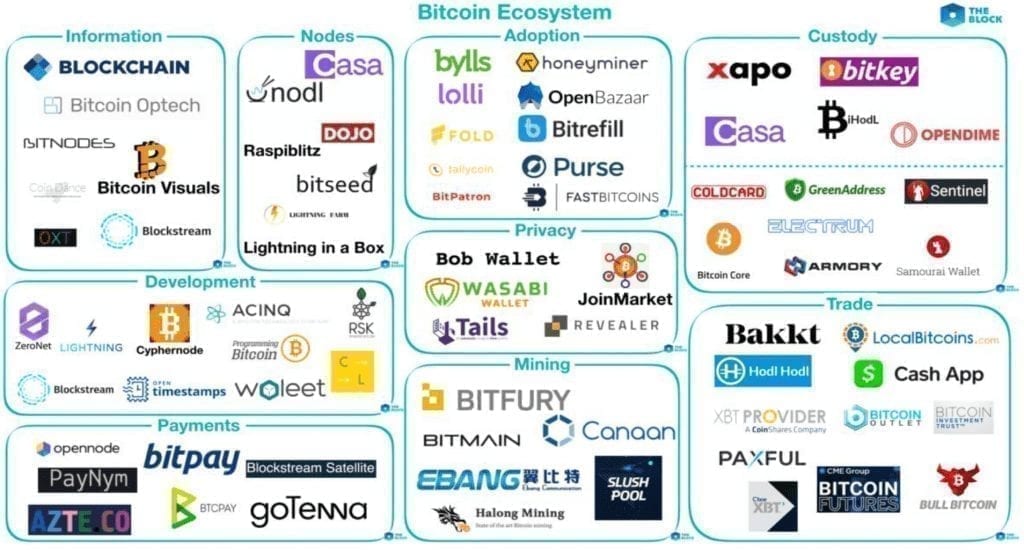
What does the future of cryptocurrencies hold for us?
It is still an uncertain future, given that the majority of presidents like Trump declare a threat to cryptocurrency by declaring that the only currency that is valid is the currency issued by the states, in his case the dollar. We are talking about an experimental technology where perhaps not everything needs blockchain and where the Uncertainty of the change caused by this new paradigm is a headache for States and companies that sooner or later will have to adapt to the change that requires structural changes (such as clocks or democracy).
Industrial Engineering student and lover of writing and technology, for several years I have participated in various pages with the aim of always keeping myself informed of the latest trends and contributing my grain of sand in this immense dissemination network that we know as the Internet.





